
Derivation of the iPS cells from fibroblasts and PBMCs using footprint-free method like mRNA and episomal plasmid reprogramming.Isolation of the peripheral blood mononuclear cells commonly called PBMCs from the blood sample.
PLURIPOTENT STEM CELLS SKIN
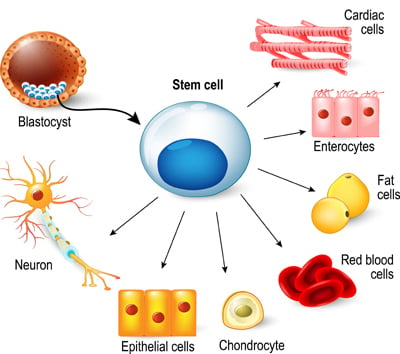
Derivation of the dermal fibroblasts from the skin biopsy.iPSCs can provide an unlimited supply of undifferentiated cells from readily available somatic, or differentiated, cells. Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), first reported in 1998, are derived directly from human embryos. The Core Facility provides the scientific community with a variety of human iPS cell lines as well as the capability of establishing and characterizing custom-made iPS cell lines from patient biopsies, utilizing state-of-the-art reprogramming techniques. The discovery of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), by Takahashi and Yamanaka in 2006, revolutionized the field of stem cell research. Induced pluripotent stem cells for cardiovascular disease modeling and precision medicine studies. Here, we provide a detailed overview of the family of pluripotent cell lines derived from early mouse and human embryos and compare them with. In addition to the ability to give rise to all cell types, a number of molecular markers have been identified to verify the pluripotent status of stem cells. However, this definition has been recently complicated by the existence of distinct cellular states that display these features. Furthermore, we show that these human neurons can reflect and capture cellular desensitization to chronic versus acute administration of dopamine. Pluripotent stem cells are cells that have the capacity to self-renew by dividing and to develop into the three primary germ cell layers of the early embryo and therefore into all cells of the. Pluripotent stem cells have the ability to undergo self-renewal and to give rise to all cells of the tissues of the body. They share many similar properties, such as pluripotency and differentiation potential, the expression of pluripotency genes, epigenetic patterns, embryoid body and teratoma formation, and viable chimera formation, but there are many differences within these properties. 2 These cells exhibit the morphology, growth, marker expression, and pluripotency of ES cells. Here through transcriptomic analysis, we map the dynamic responses of human stem cell-derived medium spiny neuron-like cells (hMSN-like cells) to dopamine. Induced pluripotent stem cells differ from embryonic stem cells. The Core Facility Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSC) serves as a source of knowledge and expertise for researchers interested in generating and working with human induced pluripotent stem cells and their differentiated progeny. Currently, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are being investigated as an alternative source for pluripotent stem cells due to their origin and. iPS cells were first generated by Takahashi and Yamanaka using mouse fibroblasts that had been transduced with four transcription factors: Oct-3/4, SOX2, c-Myc, and KLF4, under ES cell culture conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
